density of compacted vs excavated soil Bank Cubic Yards (BCY)/Bank Cubic Meters (BCM): Material as it lies in its natural bank state. Loose Cubic Yards (LCY)/Loose Cubic Meters (LCM): Material . See more Learn about the smallest mini excavators on the market in 2024, from John Deere, Bobcat and Volvo. These machines are ideal for tight spaces, transportability and versatility, with features like retractable undercarriages, electric power and zero emissions.
0 · why is bulk density important
1 · typical density of soil
2 · typical bulk density of soil
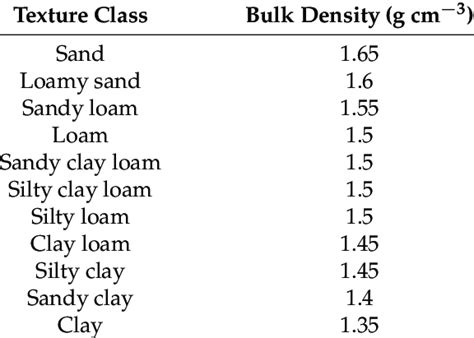
3 · soil compaction chart
4 · soil bulk density chart
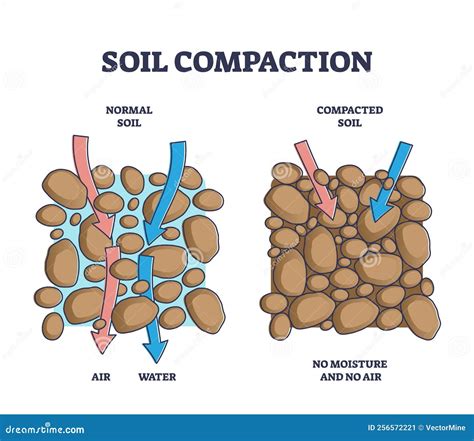
5 · how to reduce soil compaction
6 · how to determine bulk density
7 · calculate bulk density of soil
For a limited time, take advantage of 0% financing for up to 48 months* on new CASE Mini Excavators. Your CASE dealer can work with you to provide additional financing terms or alternative payment options.
Calculating appropriate volume is critical to accuracy. In-bank soil, loose soil that has been excavated and fill soil that has been compacted, have different material densities and resulting load factors. See moreCalculating appropriate volumes is critical to accuracy. In-bank soil, loose soil that has been excavated and fill soil that has been compacted, have different volumes . See moreBank Cubic Yards (BCY)/Bank Cubic Meters (BCM): Material as it lies in its natural bank state. Loose Cubic Yards (LCY)/Loose Cubic Meters (LCM): Material . See more*Weight of material varies with moisture content, grain size, degreee of compaction, etc. Tests must be made to determine exact material characteristics. . See more
Learn how to calculate the volume and weight of moist and dry granular materials using bulking factor and bulk density. Find tables of typical values for different types of soils, rocks, and .Find typical values of soil densities and elastic modulus for different soil types and phases. Learn how to use soil properties for foundation design and analysis with caution and factor of safety. Learn how to measure the in-situ density of soil using the sand replacement method. The in-situ density is the weight of the excavated soil divided by the in-situ volume, .Learn about soil compaction, the densification of soils by removal of air through mechanical energy. Find out the optimum moisture content, maximum dry unit weight, and compaction .
Learn about soil compaction, the method of mechanically increasing the density of soil, and its importance in construction. Find out how to identify and classify different soil types, and the . Learn how to design and measure earthwork for roadway excavation and embankment on federal lands. Find formulas, factors, and tables for different types of material .Learn how to measure and interpret soil bulk density, a dynamic property that reflects the compactness and porosity of soil. Find out how bulk density varies with texture, organic .
Learn what soil bulk density is, how to measure it using core or excavation methods, and how to calculate relative bulk density as an index of soil compaction. Find out the factors that affect .Estimating earthwork involves quantity measures in three different volume/density states: (1) a soil at its native undisturbed density is measured in bank cubic yards (BCY); (2) the same soil that .Find the density of soil in kg/m3 for different types of soil, such as clay, sand, gravel, and earth, in loose and bank conditions. Compare the load factors and volume calculations for excavation and compaction.
Learn how to calculate the volume and weight of moist and dry granular materials using bulking factor and bulk density. Find tables of typical values for different types of soils, rocks, and quarry products.Find typical values of soil densities and elastic modulus for different soil types and phases. Learn how to use soil properties for foundation design and analysis with caution and factor of safety.Learn how to measure the in-situ density of soil using the sand replacement method. The in-situ density is the weight of the excavated soil divided by the in-situ volume, and it is used to control the compaction of soil or pavement layers.Learn about soil compaction, the densification of soils by removal of air through mechanical energy. Find out the optimum moisture content, maximum dry unit weight, and compaction curves for different soil types and methods.

why is bulk density important
Learn about soil compaction, the method of mechanically increasing the density of soil, and its importance in construction. Find out how to identify and classify different soil types, and the best compaction methods and techniques for each type. Learn how to design and measure earthwork for roadway excavation and embankment on federal lands. Find formulas, factors, and tables for different types of material and conditions.Learn how to measure and interpret soil bulk density, a dynamic property that reflects the compactness and porosity of soil. Find out how bulk density varies with texture, organic matter, depth and management.Learn what soil bulk density is, how to measure it using core or excavation methods, and how to calculate relative bulk density as an index of soil compaction. Find out the factors that affect soil bulk density and the reference values for optimal crop and tree growth.
Estimating earthwork involves quantity measures in three different volume/density states: (1) a soil at its native undisturbed density is measured in bank cubic yards (BCY); (2) the same soil that has been excavated typically has a lower relative density (its volume increases) and is measured in loose ("haul" or "truck") cubic yards (LCY); and .
Find the density of soil in kg/m3 for different types of soil, such as clay, sand, gravel, and earth, in loose and bank conditions. Compare the load factors and volume calculations for excavation and compaction.
Learn how to calculate the volume and weight of moist and dry granular materials using bulking factor and bulk density. Find tables of typical values for different types of soils, rocks, and quarry products.Find typical values of soil densities and elastic modulus for different soil types and phases. Learn how to use soil properties for foundation design and analysis with caution and factor of safety.
Learn how to measure the in-situ density of soil using the sand replacement method. The in-situ density is the weight of the excavated soil divided by the in-situ volume, and it is used to control the compaction of soil or pavement layers.Learn about soil compaction, the densification of soils by removal of air through mechanical energy. Find out the optimum moisture content, maximum dry unit weight, and compaction curves for different soil types and methods.

Learn about soil compaction, the method of mechanically increasing the density of soil, and its importance in construction. Find out how to identify and classify different soil types, and the best compaction methods and techniques for each type.
Learn how to design and measure earthwork for roadway excavation and embankment on federal lands. Find formulas, factors, and tables for different types of material and conditions.
Learn how to measure and interpret soil bulk density, a dynamic property that reflects the compactness and porosity of soil. Find out how bulk density varies with texture, organic matter, depth and management.Learn what soil bulk density is, how to measure it using core or excavation methods, and how to calculate relative bulk density as an index of soil compaction. Find out the factors that affect soil bulk density and the reference values for optimal crop and tree growth.
tractor or skid steer for farm
typical density of soil
LEGO 7246 Mini Digger instructions displayed page by page to help you build this amazing LEGO City Construction set.
density of compacted vs excavated soil|soil compaction chart